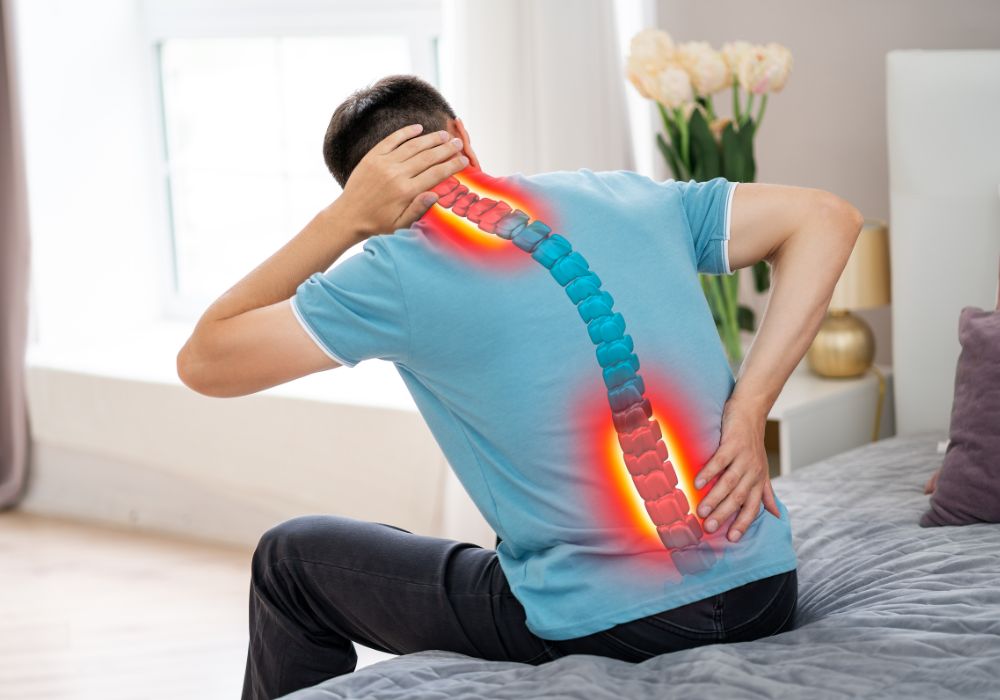
Lumbar Spondylitis
What it is?
Lumbar spondylitis, also known as lumbar spondylosis or lumbar osteoarthritis, is a degenerative condition that affects the lumbar spine. It involves the breakdown of the cartilage and bones in the lower back, particularly the vertebrae and the discs between them.
This condition is commonly seen in older individuals and is a natural part of the aging process. But it is very often seen in young adults these days. Certain factors can contribute to an increased risk of developing lumbar spondylitis, such as obesity, smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, and previous injuries to the spine.
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of lumbar spondylitis usually involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to assess the extent of the degenerative changes in the lumbar spine.
Treatment for lumbar spondylitis focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further degeneration of the spine. Conservative treatment options may include:
– Pain management through over-the-counter or prescription medications.
– Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility.
– Low-impact exercises such as swimming or walking.
– Heat or cold therapy to alleviate pain and stiffness.
– Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and adopting good posture.
– Assistive devices like braces or orthotics to support the lower back.
What to do?
If symptoms are severe or conservative measures fail, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgery options can include removing bone spurs, decompressing nerves, or even spinal fusion to stabilize the affected area.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or spine specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for individual cases of lumbar spondylitis.
This condition is commonly seen in older individuals and is a natural part of the aging process. But it is very often seen in young adults these days . Certain factors can contribute to an increased risk of developing lumbar spondylitis, such as obesity, smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, and previous injuries to the spine.
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of lumbar spondylitis usually involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to assess the extent of the degenerative changes in the lumbar spine.
Treatment for lumbar spondylitis focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further degeneration of the spine. Conservative treatment options may include:
– Pain management through over-the-counter or prescription medications.
– Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility.
– Low-impact exercises such as swimming or walking.
– Heat or cold therapy to alleviate pain and stiffness.
– Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and adopting good posture.
– Assistive devices like braces or orthotics to support the lower back.
What to do?
If symptoms are severe or conservative measures fail, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgery options can include removing bone spurs, decompressing nerves, or even spinal fusion to stabilize the affected area.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or spine specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for individual cases of lumbar spondylitis.
Patient Testimonials
Orthoderm brings a wealth of knowledge, a depth of understanding, and a shared commitment to patient-centered care.

Manish Agrawal

Karishma Konwar

Hirak Jyoti Sarmah

Manish Agrawal

Karishma Konwar
Contact Dr. Anish Agarwalla
Orthoderm brings a wealth of knowledge, a depth of understanding, and a shared commitment to patient-centered care.