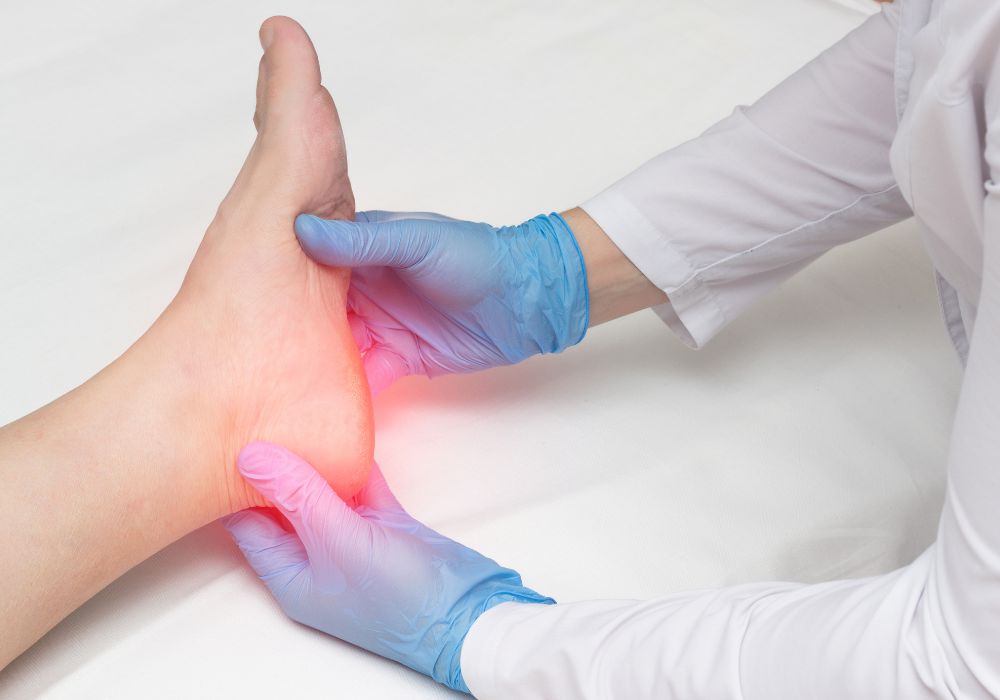
Plantar Fasciitis
What it is?
Symptoms
Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis, including:
1. Overuse or repetitive strain: Activities that put stress on the feet, such as running, jumping, or standing for long periods, can lead to plantar fasciitis.
2. Foot mechanics: Flat feet, high arches, or abnormal walking patterns can increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
3. Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the plantar fascia, increasing the risk of inflammation.
4. Age: Plantar fasciitis is more common in middle-aged adults.
Diagnosis
1. Rest and modification of activities: Avoiding activities that worsen the pain can help with the healing process.
2. Ice and over-the-counter pain relievers: Applying ice to the affected area and taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
3. Stretching and strengthening exercises: Stretching the calf muscles and plantar fascia can help relieve tension and promote healing. Strengthening exercises may also be recommended to improve foot stability.
4. Orthotics and support devices: Wearing supportive shoes with cushioned arch supports or using custom orthotic inserts can provide additional support and relieve stress on the plantar fascia.
5. Physical therapy: In severe cases, physical therapy may be recommended to promote healing and improve foot mechanics.
In most cases, plantar fasciitis can be effectively treated with conservative measures. However, in rare cases, surgical interventions may be necessary if conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
Plantar Fasciitis
What it is?
Symptoms
Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis, including:
1. Overuse or repetitive strain: Activities that put stress on the feet, such as running, jumping, or standing for long periods, can lead to plantar fasciitis.
2. Foot mechanics: Flat feet, high arches, or abnormal walking patterns can increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
3. Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the plantar fascia, increasing the risk of inflammation.
4. Age: Plantar fasciitis is more common in middle-aged adults.
Diagnosis
1. Rest and modification of activities: Avoiding activities that worsen the pain can help with the healing process.
2. Ice and over-the-counter pain relievers: Applying ice to the affected area and taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
3. Stretching and strengthening exercises: Stretching the calf muscles and plantar fascia can help relieve tension and promote healing. Strengthening exercises may also be recommended to improve foot stability.
4. Orthotics and support devices: Wearing supportive shoes with cushioned arch supports or using custom orthotic inserts can provide additional support and relieve stress on the plantar fascia.
5. Physical therapy: In severe cases, physical therapy may be recommended to promote healing and improve foot mechanics.
In most cases, plantar fasciitis can be effectively treated with conservative measures. However, in rare cases, surgical interventions may be necessary if conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
Patient Testimonials
Orthoderm brings a wealth of knowledge, a depth of understanding, and a shared commitment to patient-centered care.

Manish Agrawal

Karishma Konwar

Hirak Jyoti Sarmah

Manish Agrawal

Karishma Konwar
Contact Dr. Anish Agarwalla
Orthoderm brings a wealth of knowledge, a depth of understanding, and a shared commitment to patient-centered care.